Create Predicted Eventlog
This article has instructions how to install, configure and use eventlog predictions. The prediction creates a new model that contains the source model data and the predictions. It's able to predict case attributes for the generated new cases and event attributes for the predicted events. To distinguish the real (source data) and predicted events and cases, there are following attributes in the model:
- Event attribute Predicted denotes whether the event is from the source data (false) or whether it's predicted (true).
- Case attribute Generated denotes whether the case is in the source data (false) or whether the prediction generated it as a new case (true).
Prerequisites for prediction
Following prerequisites need to be fulfilled to run the eventlog prediction:
- QPR ProcessAnalyzer 2024.2 or later in use
- Snowflake connection is configured
- Source models are stored to Snowflake
Install prediction to Snowflake
To install the eventlog prediction to Snowflake:
- Go to Snowflake, and create a Snowflake-managed stage with name PREDICTION to the same schema configured to QPR ProcessAnalyzer (in the Snowflake connection string). Use settings in the following image:
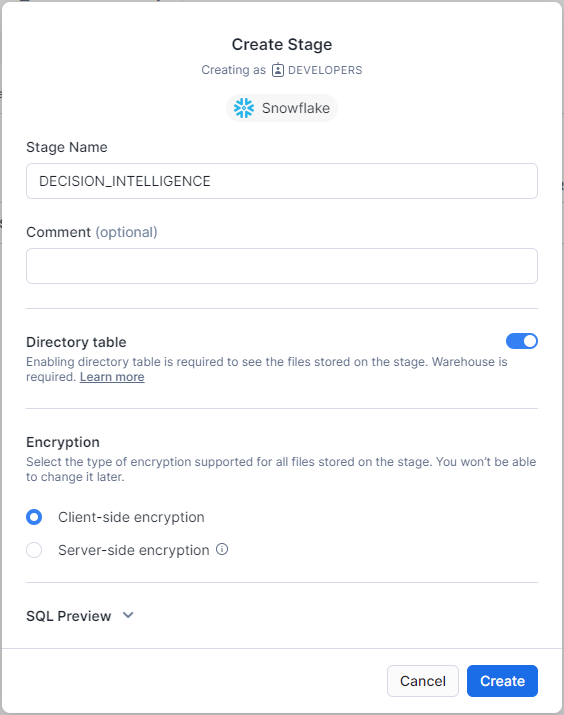
- Open the created stage and upload the predict.pyz file into the stage (ask the file from your QPR representative).
- Create the following procedure to the same schema:
CREATE OR REPLACE PROCEDURE QPRPA_SP_PREDICTION("CONFIGURATION" OBJECT)
RETURNS OBJECT
LANGUAGE PYTHON
STRICT
RUNTIME_VERSION = '3.8'
PACKAGES = ('nltk','numpy','pandas==1.5.3','scikit-learn','snowflake-snowpark-python','tensorflow','dill','prophet','holidays==0.18','python-kubernetes','docker-py')
HANDLER = 'main'
EXECUTE AS OWNER
AS '
import sys
def main(session, parameters_in: dict) -> dict:
session.file.get(''@decision_intelligence/predict.pyz'', ''/tmp'')
sys.path.append(''/tmp/predict.pyz'')
import predict
return predict.main(session, parameters_in)
';
Create prediction script in QPR ProcessAnalyzer
1. Create the following example expression script (e.g., with name Create prediction model):
let sourceModel = ProjectByName("<project name>").ModelByName("<model name>");
let completeCaseEventTypeName = "<event type name found only in complete cases>";
let targetProject = Project;
let eventTypeColumnName = sourceModel.EventsDataTable.ColumnMappings["EventType"];
_system.ML.GeneratePredictionModel(#{
"Name": "My prediction model", // Name of the PA model to generate ti the target project.
"SourceModel": sourceModel, // Snowflake-based PA model used for training the prediction model.
"TargetProject": targetProject, // Target project to create the model into.
"TrainingConfiguration": #{ // Training parameters.
"num_epochs_to_train": 200
},
"GenerationConfiguration": #{ // Model generation parameters.
"cases_to_generate": 1000
},
"TrainingDataFilter": #{
"Items": [
#{
"Type": "IncludeCases",
"Items": [
#{
"Type": "EventAttributeValue",
"Attribute": eventTypeColumnName,
"StringifiedValues": [
`0${completeCaseEventTypeName}`
]
}
]
}
]
},
"IncompleteCasesFilter": #{
"Items": [
#{
"Type": "ExcludeCases",
"Items": [
#{
"Type": "EventAttributeValue",
"Attribute": eventTypeColumnName,
"StringifiedValues": [
`0${completeCaseEventTypeName}`
]
}
]
}
]
},
"RecreatePredictionModel": true, // Should a prediction model be overwritten if one already exists for this source model and target model name combination.
"TrainingCaseSampleSize": 10000 // Maximum number of cases to use from the source model (random sampled).
});
2. Configure prediction for the previously created script as instructed in the next chapter. At minimum, replace the tags listed below with some suitable values:
- <project name>: Name of the project in which the source model is located.
- <model name>: Name of the model to be used as source model. This data in this source model will be used to train the prediction model so that it can generate new cases and continuations for incomplete existing cases.
- <event type name found only in complete cases>: This example script has been hard-coded to determine whether a case is complete or incomplete based on the existence of this event type.
Configure prediction
Prediction script has the following settings in the GeneratePredictionModel call:
- Name: Name of the QPR ProcessAnalyzer model that is created to the target project. The model will contain the source model content and the predictions.
- SourceModel: Source model for which the prediction is made. Model can be selected for example based on id with ModelById function or by name with ModelByName function.
- TargetProject: Target project to create the new model into.
- RecreatePredictionModel: When true, a new ML model is trained when the script is run. When false, the prediction is run using possibly pre-existing ML model.
- TrainingConfiguration: Training parameters.
- num_epochs_to_train: How many times the whole training data is used in training. The more there are epochs, the better the model usually is, but the training will take more time. The best performing model out of all the iterations will be selected.
- max_num_case_clusters: Maximum number of clusters to divide the case attribute values into. Default is 20.
- GenerationConfiguration: Event generation parameters. When null, no generation is done. For example, following parameters are supported:
- cases_to_generate: Maximum number cases to create. The number of created cases is further limited by the capabilities of the trained model and the case_generation_start_time and case_generation_end_time parameters.
- case_generation_start_time: If defined, new cases will be generated starting from this timestamp. If not defined, the latest start event timestamp used in the training data. This parameter is given as ISO datetime format.
- case_generation_end_time: If defined, the new cases generation will stop when reaching this timestamp, and no cases will be generated after it. This parameter is given as ISO datetime format.
- generate_debug_event_attributes: If true, additional columns will be added containing, e.g., probabilities of the selected activity and other activities.
- min_prediction_probability : Minimum probability of any activity name in next activity prediction. If the probability of an activity is lower than this, it will never be picked. Default value is 0.01.
- temperature: If 0, the predicted event type will always be the most probable one. If 1, the next event type is randomly selected based on probabilities of each event type. This behavior is interpolated when using values between 0 and 1.
- TrainingDataFilter: Filter to select specific cases that are used to train the prediction model. This filter is required to train the model only using the completed cases. Uncompleted cases should not be used for the training, so the model doesn't incorrectly learn that cases should end like that.
- IncompleteCasesFilter: Optional filter to select which cases the prediction is made for. To improve performance of the prediction, it's recommended to include only the incomplete cases for which new events might appear, and skip the completed cases for which new events are not expected anymore.
- TrainingCaseSampleSize: Maximum number of cases to take from the source model (cases are selected randomly). Use a lower setting to speed up the ML model training. The greater the value, the more subtle phenomena the prediction can learn from the data.