Chart Linked Settings: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
The linked settings are used to bind chart settings, so that the bound maintain same values. When any of the bound settings is changed, other linked settings get also changed. The bound settings are defined to a linked settings group, and there can be several of these groups in the chart. | |||
Linked settings are | == Usage == | ||
* '''type''': One of the following type of | Tips when creating linked settings: | ||
* Make sure to bind only settings that are of same data type. For example trying to bind strings and integers will likely not work. An exception is that it's possible to bind string array and individual string value, because the individual value is automatically converted into an array of a single value. | |||
* Finding the correct technical setting name requires to look at the chart settings json (in the ''Advanced'' tab). The label names in the settings dialog is not necessary the technical name that needs to be used in the linked settings. | |||
* It's possible to define as many linked settings to the group as needed. Obviously, there needs to be at least two settings, for the linked settings to work meaningfully. Likewise, there can be as many linked setting groups in the same chart as needed. | |||
== Configuration == | |||
Linked settings are configured in the '''Advanced''' tab of chart/flowchart by clicking '''Linked settings'''. Linked settings json consists of ''setting groups'' which are array of objects. Each object points to an individual setting having the following properties: | |||
* '''type''': One of the following type of setting: | |||
** '''measure''': For measure parameters. | ** '''measure''': For measure parameters. | ||
** '''dimension''': For dimension and column parameters. | ** '''dimension''': For dimension and column parameters. | ||
** '''eventtypemeasure''': For flowchart event measures. | ** '''eventtypemeasure''': For flowchart event measures. | ||
** '''flowmeasure''': For flowchart flow measures. | ** '''flowmeasure''': For flowchart flow measures. | ||
** '''root''': | ** '''root''': For analyzed objects parameters. | ||
** '''generic''': For other chart settings. | ** '''generic''': For other chart settings. | ||
** '''tag''': For binding to a tag. | ** '''tag''': For binding to a tag. Tags can be used in the custom expressions. | ||
** '''variable''': For binding to a dashboard variable. | ** '''variable''': For binding to a dashboard variable. | ||
** '''filtervalue''': For binding to | ** '''filtervalue''': For binding to filter rule parameters. | ||
** '''filterattribute''': For binding to | ** '''filterattribute''': For binding to case or event attribute name in filter rule. | ||
* '''index''': | * '''index''': Defines the order number (starts from 0), when ''type'' is a ''measure'', ''dimension'', ''eventtypemeasure'' or ''flowmeasure''. | ||
* '''parameter''': Name of the chart setting or parameter. | * '''parameter''': Name of the chart setting or parameter. | ||
* '''tagName''': When ''type'' is ''tag'', defines the | * '''tagName''': When ''type'' is ''tag'', defines the bound tag name. The tag can be used in custom expressions similar to variables with syntax <#MyTagName>. Linking to tags is one-way: when a setting is changed, the tag is changed accordingly. On the other hand, the tag value itself cannot be changed directly. | ||
* '''variableName''': When linked setting type is ''variable'', defines the variable name. Linking to variables is two-way: when a variable value | * '''variableName''': When linked setting type is ''variable'', defines the variable name. Linking to variables is two-way: when a variable value is changed, the other linked setting is changed accordingly, and when the other setting is changed, a linked variable value is changed accordingly. | ||
* '''filterGroupType''': | * '''filterGroupType''': When ''type'' is ''filtervalue'' or ''filterattribute'', defines the filter group type (''IncludeCases'', ''ExcludeCases'', ''IncludeEvents'', ''ExcludeEvents'', ''IncludeEventTypes'', ''ExcludeEventTypes''). | ||
* '''filterRuleType''': | * '''filterRuleType''': When ''type'' is ''filtervalue'' or ''filterattribute'', defines the filter rule type (''CaseAttributeValue'', ''EventAttributeValue'', ''Attribute'', ''EventType'', ''Case''). | ||
* '''attribute''': | * '''attribute''': When ''type'' is ''filterattribute'', defines the attribute name. Used for filter rule types ''CaseAttribute'', ''EventAttribute'' and ''Attribute''. | ||
If referring to an expression level filter, parameters expressionCategory (measure/dimension/eventtypemeasure/flowmeasure) and index are to be defined. When these parameters are not defined, the linked setting refers to a chart level filter rule. Filter rule that matches with the filterGroupType and filterRuleType is used. If no matching filter rule exist, a new filter rule is created, when setting the property. | If referring to an expression level filter, parameters expressionCategory (measure/dimension/eventtypemeasure/flowmeasure) and index are to be defined. When these parameters are not defined, the linked setting refers to a chart level filter rule. Filter rule that matches with the filterGroupType and filterRuleType is used. If no matching filter rule exist, a new filter rule is created, when setting the property. | ||
== Examples == | |||
=== Measure and dimension parameters === | |||
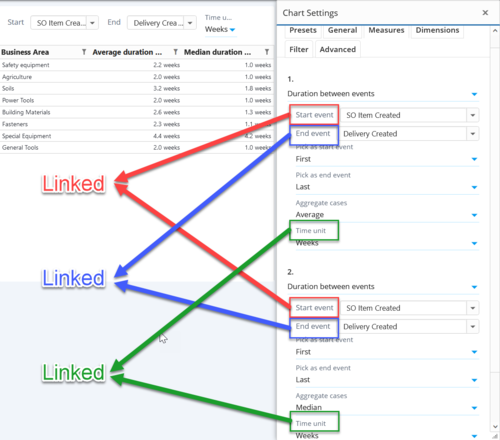
[[File:Linkedsettings.png|center|500px]] | [[File:Linkedsettings.png|center|500px]] | ||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
| Line 65: | Line 73: | ||
] | ] | ||
] | ] | ||
</pre> | |||
=== Analyzed objects parameters === | |||
<pre> | |||
</pre> | |||
=== Generic settings === | |||
<pre> | |||
</pre> | |||
=== Filter rules=== | |||
<pre> | |||
</pre> | |||
=== Variables === | |||
<pre> | |||
</pre> | |||
=== Tags === | |||
<pre> | |||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
Revision as of 23:21, 20 December 2022
The linked settings are used to bind chart settings, so that the bound maintain same values. When any of the bound settings is changed, other linked settings get also changed. The bound settings are defined to a linked settings group, and there can be several of these groups in the chart.
Usage
Tips when creating linked settings:
- Make sure to bind only settings that are of same data type. For example trying to bind strings and integers will likely not work. An exception is that it's possible to bind string array and individual string value, because the individual value is automatically converted into an array of a single value.
- Finding the correct technical setting name requires to look at the chart settings json (in the Advanced tab). The label names in the settings dialog is not necessary the technical name that needs to be used in the linked settings.
- It's possible to define as many linked settings to the group as needed. Obviously, there needs to be at least two settings, for the linked settings to work meaningfully. Likewise, there can be as many linked setting groups in the same chart as needed.
Configuration
Linked settings are configured in the Advanced tab of chart/flowchart by clicking Linked settings. Linked settings json consists of setting groups which are array of objects. Each object points to an individual setting having the following properties:
- type: One of the following type of setting:
- measure: For measure parameters.
- dimension: For dimension and column parameters.
- eventtypemeasure: For flowchart event measures.
- flowmeasure: For flowchart flow measures.
- root: For analyzed objects parameters.
- generic: For other chart settings.
- tag: For binding to a tag. Tags can be used in the custom expressions.
- variable: For binding to a dashboard variable.
- filtervalue: For binding to filter rule parameters.
- filterattribute: For binding to case or event attribute name in filter rule.
- index: Defines the order number (starts from 0), when type is a measure, dimension, eventtypemeasure or flowmeasure.
- parameter: Name of the chart setting or parameter.
- tagName: When type is tag, defines the bound tag name. The tag can be used in custom expressions similar to variables with syntax <#MyTagName>. Linking to tags is one-way: when a setting is changed, the tag is changed accordingly. On the other hand, the tag value itself cannot be changed directly.
- variableName: When linked setting type is variable, defines the variable name. Linking to variables is two-way: when a variable value is changed, the other linked setting is changed accordingly, and when the other setting is changed, a linked variable value is changed accordingly.
- filterGroupType: When type is filtervalue or filterattribute, defines the filter group type (IncludeCases, ExcludeCases, IncludeEvents, ExcludeEvents, IncludeEventTypes, ExcludeEventTypes).
- filterRuleType: When type is filtervalue or filterattribute, defines the filter rule type (CaseAttributeValue, EventAttributeValue, Attribute, EventType, Case).
- attribute: When type is filterattribute, defines the attribute name. Used for filter rule types CaseAttribute, EventAttribute and Attribute.
If referring to an expression level filter, parameters expressionCategory (measure/dimension/eventtypemeasure/flowmeasure) and index are to be defined. When these parameters are not defined, the linked setting refers to a chart level filter rule. Filter rule that matches with the filterGroupType and filterRuleType is used. If no matching filter rule exist, a new filter rule is created, when setting the property.
Examples
Measure and dimension parameters
[
[
{
"type": "measure",
"index": 0,
"parameter": "Start event"
},
{
"type": "measure",
"index": 1,
"parameter": "Start event"
}
],
[
{
"type": "measure",
"index": 0,
"parameter": "End event"
},
{
"type": "measure",
"index": 1,
"parameter": "End event"
}
],
[
{
"type": "measure",
"index": 0,
"parameter": "Time unit"
},
{
"type": "measure",
"index": 1,
"parameter": "Time unit"
}
]
]